In this story we will show you how to use the GitHub extension for JupyterLab. GitHub provides a central repository for your code and allows you to track changes across versions. With the extension you can easily review files and see the changes made by your team. This assumes you have the JupyterHub for Collaboration image deployed which we discussed in a previous story. For a list of all JupyterHub collaboration stories see Data Science Team Collaboration with JupyterHub and JupyterLab.
You can use a public repository to evaluate the extension like SocialHealthAI/Education. Or to set up a repository see: Create a repo — GitHub Docs. For authentication you will need to set up an SSH key or personal access token. GitHub recommends a personal access token as they have afiner grain control. See: Personal access tokens. Note that authentication is not necessary if you just want to clone a public repository.
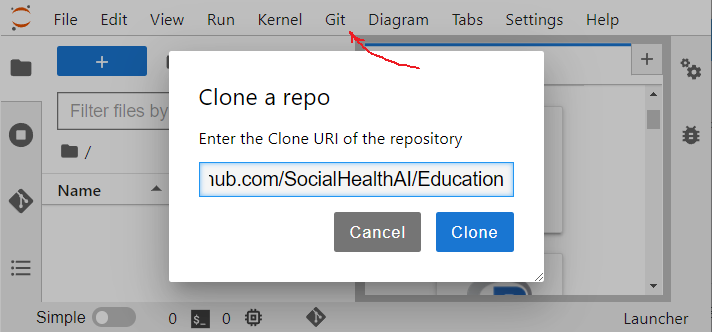
Use the JupyterLab Git menu to clone a repository.
Now open a notebook using the File Browser. For example, open the Logistic_Regression_Demo notebook in the above SocialHealth/Education repo. Change the pairplot to use “class” instead of “fare” to color the plots.
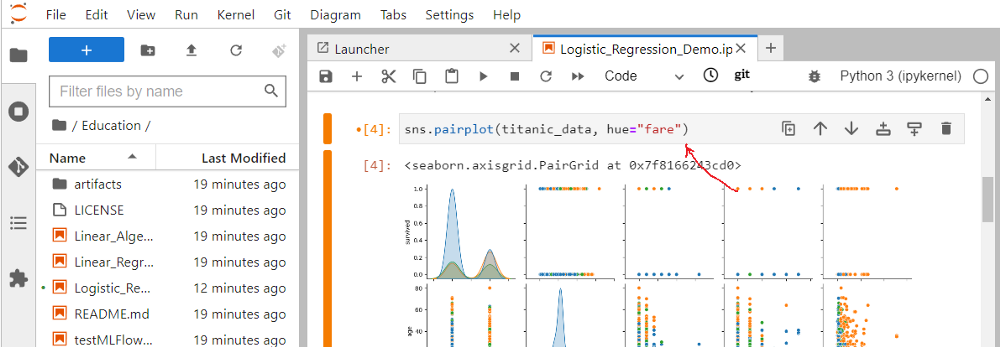
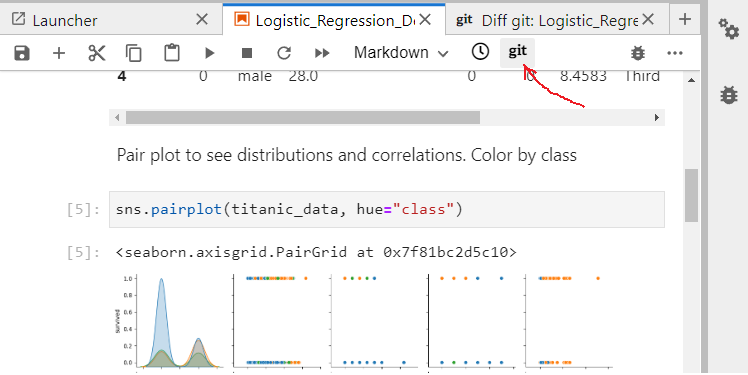
Run the first four code cells, save the notebook and select the git view:
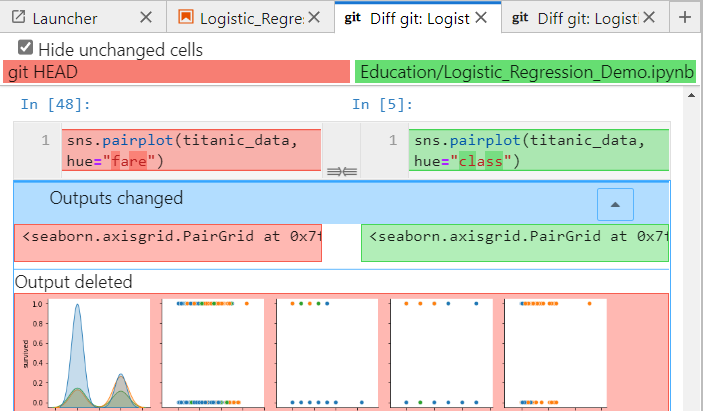
The Diff git view shows changes to the code and markdown cells. And it shows outputs deleted and added. If you were to review changes with another diff tool or changes using the GitHub site they would not very useful as notebooks are json files. The GitHub extension for JupyterLab shows changes to the cell contents and the new outputs instead of showing changes to the json file. So you can easily review your updates before committing them to GitHub and share them with the team.
Selecting the git icon on the left, you can review your staged, changed and untracked files. You can then stage the changed files and commit them.

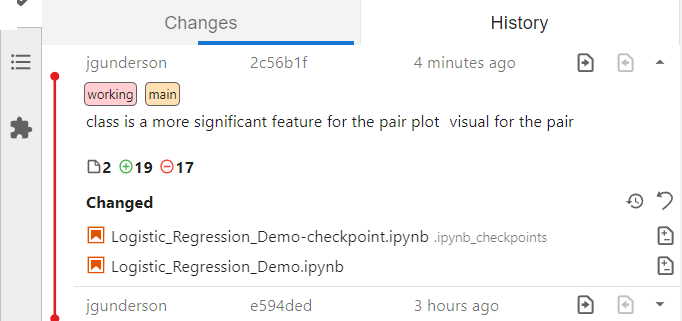
If you select the History panel you review the changes in each push to the repository and each branch. You can see the detail and reasons behind the changes made by your team members.
The GitHub extension for JupyterLab has many of the Git functions you will need. For Git functions not supported you can Open Git Repository from Terminal using the Git menu. For example, to create a new branch:

For more information on the GitHub extension for JupyterLab, see A Git extension for JupyterLab .

No responses yet